Pendle Finance just launched its v2 and this post will breakdown all you need to know regarding changes to the protocol and the token.
Introduction – What is Pendle Finance?
In short, Pendle can be seen as an interest rate DEX allowing users to trade the future interest of a yield bearing token. Some terminologies to take note before diving deeper:
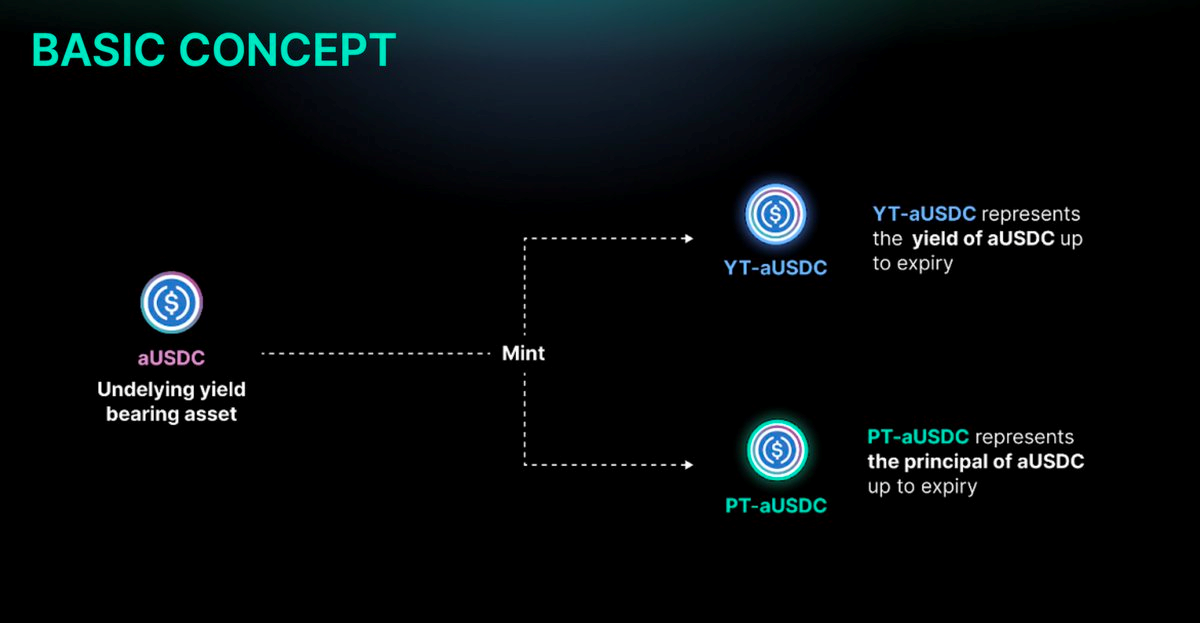
- Yield bearing tokens: these are tokens that generate yield and act as a proof of deposit. For example, supplying USDC in Aave gets you aUSDC which represents ownership of the loan and can be used to claim the original deposit (that is earning yield).
- Principal Token (PT): the underlying yield bearing token
- Yield token (YT): the implied yield that is generated over time
- Contract: duration for which maturity is reached
- Maturity: the date at which PT becomes fully redeemable for the underlying asset (yield bearing token) and YT stops accruing yield
User interaction with Pendle
Users receive PTs and YTs after depositing their yield bearing token into the platform which they will have to set a maturity date. This date decides when each PT is redeemable 1:1 for the deposited yield bearing token and when the YT becomes worthless (at maturity, there is no yield to earn).
How each user perceives the future interest rate payout will determine their interaction with Pendle. For example, if a user believes that interest rates will fall in the future due to worsening market conditions, he may opt to swap the YT into more PT to secure the initial yield. Or if a user is bullish on an interest rate appreciation, he can take a leveraged position on the yield by selling PT into more YT.
Different strategies exist for various stakeholders:
- Traders: able to leverage yield opportunities without locking up principle as shown above
- Arbitrageurs: profit by rebalancing the market inside Pendle’s custom AMM engine
- Liquidity providers: provide liquidity on the Pendle AMM for yield (swap fees, protocol incentives, PT fixed-rate interest)
Pendle therefore allows users to maximise their yield in the ever erratic market with constant yield fluctuations. Yield exposure can be increased during bull markets by buying more YT and hedge against yield downturns during bear markets by buying more PT.
Last month, Pendle released a host of improvements to its protocol and its v2 design consists of changes to its AMM, yield token standard and tokenomics all of which will be covered more in detail below.
Pendle AMM
In v1, Pendle allowed users to participate in various strategies upon receiving the YT. They could deposit the YT into a liquidity pool (YT-USDC pair) to allow other users to buy or sell the YT against USDC. In return, these liquidity providers get rewarded in governance tokens and swap fees. Alternatively, users could sell the YT back to USDC (using the same pool) and use it to either get more interest bearing tokens (by depositing the USDC back into Aave) or purchasing other tokens (i.e. using the FUTURE yield of a token to make a CURRENT purchase).
However, because the value of YT is not constant (due to demand and supply of the token), liquidity providers face impermanent losses from the price fluctuations. To eliminate this, Pendle’s new AMM will only allow LPs to provide PTs and the yield bearing token (instead of the YT as in V1) both of which are closely correlated. LPs will earn:
- Fixed yield from the PT supplied to the pool
- Yields from yield bearing tokens provided
- Swap fees (from both PT and YT trades)
- PENDLE incentives
In v1, there was capital fragmentation as the platform required 2 separate pools for trading PT and YT. Now, PTs and YTs can be traded using a single pool of PT liquidity, enabled by utilising flash swaps. Two scenarios of flash swaps:
- Bullish YT: a buyer wants to buy more YT as he thinks it is relatively cheap, thus he sends yield bearing token (source token) into the swapping contract which withdraws more of the token from the pool (borrow) to mint both PT and YT. YT is sent to the buyer while the PT is sold to the pool for more of the yield bearing token to repay the loan (rebalance the pool).
- Bearish YT: seller wants to sell YT as he thinks the yield has peaked, thus he sends the YT to the swap contract which borrows an equivalent amount of PT from the pool. Both YT and PT are then used to redeem for the yield bearing token (source token). Seller gets some of the source token, while the rest is sent back to the pool to repay some of the PT that was borrowed.
More info on flash swaps: https://docs.pendle.finance/PendlePro/HowItWorks/AMM.
Liquidity on the AMM will also be enhanced through two improvements – concentrated liquidity and dynamic curves:
- Concentrated liquidity: Pendle is able to estimate the rough yield range of an asset to enable concentrated liquidity within a particular range. Inspired by Uniswap v3, this allows for more efficient usage of capital and better liquidity for the AMM
- Dynamic curve: AMM curve automatically shifts to factor in the changes in PT and YT prices as they near maturity so that only the interest rate changes are traded and not the prices of the individual tokens

Other improvements to the AMM include include:
- Auto-routing, allowing users to trade or LP for PTs/YTs with any major asset
- Dynamic fee rate where fees are based on interest rates instead of the absolute amount
- Gas optimization for better cost efficiency
- TWAP oracle to ensure composability of fixed-rate products on the platform
New token standard – EIP5115
Yield generating mechanisms are built in all sorts of forms, and this requires projects to manually integrate them every time a protocol builds on top of another protocol’s yield generating mechanism. This makes building protocols on top of yield assets very difficult due to the fragmentation and time-consuming as developers have to account for many different yield-generating mechanics. Yield markets are therefore not fully permissionless.
In v2, Pendle will incorporate the new token standard EIP5115 (super composable yield token) also known as Standardise Yield (SY) that wraps all yield bearing tokens into a single standardised yield interface.
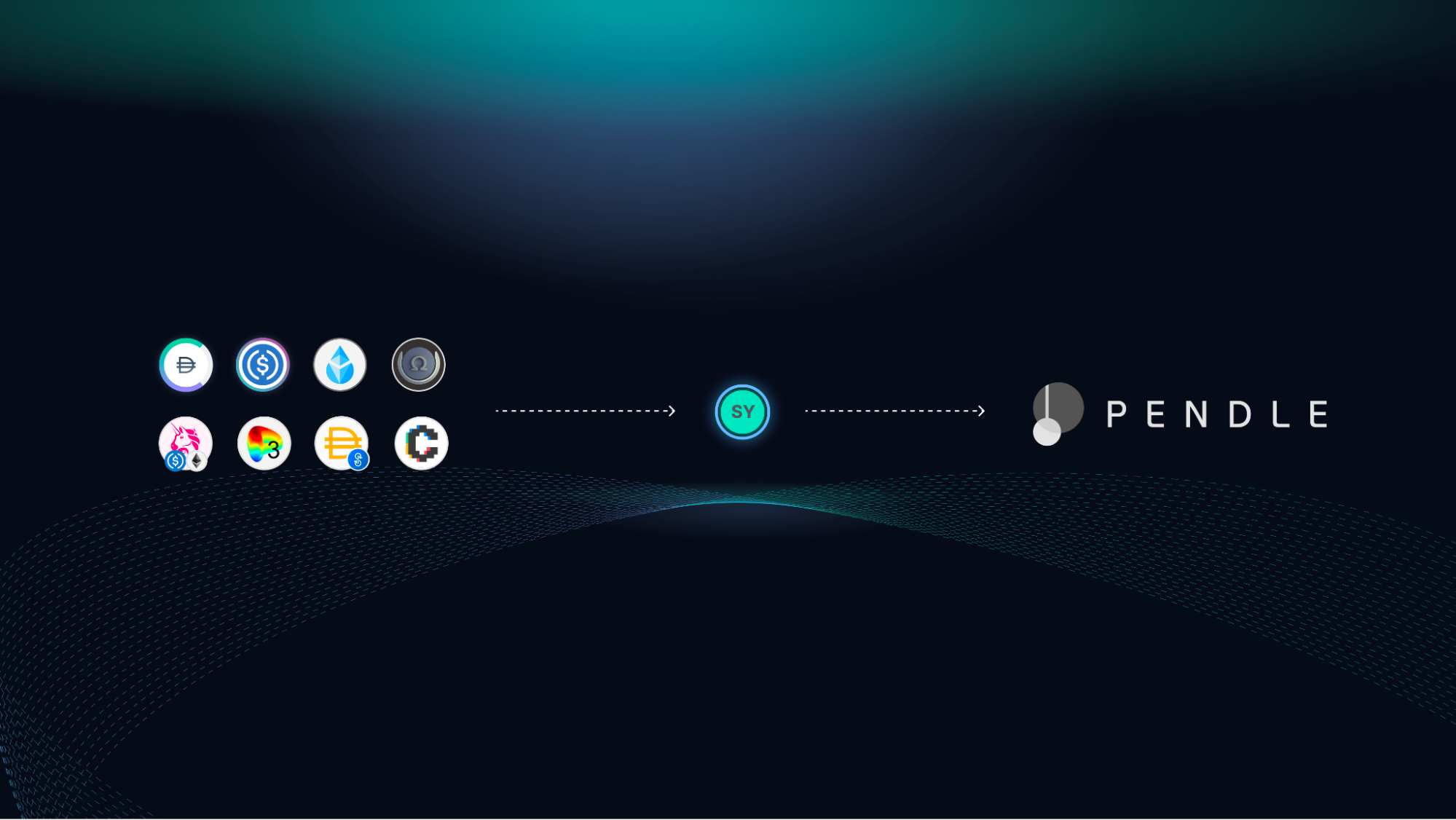
With this standard, developers can not only access vault and lending tokens but also staking tokens (e.g. stETH) and LP tokens. SY aims to create unprecedented composability across all of DeFi where other protocols can build on top of their SY token. This also ensures that yield markets are permissionless. More info on EIP-5115: https://eips.ethereum.org/EIPS/eip-5115
Pendle is also widening its horizon as it goes crosschain having integrated with both LayerZero and Kyber Network. This allows Pendle to scale and serve other target segments of the yield market. Currently, the platform is live on both Ethereum mainnet and Avalanche.
Tokenomics revamp
The previous iteration of the $PENDLE token lacked utility within the protocol. With V2, $PENDLE gets a full revamp and provides more utility to holders with vote-escrowed tokenomics:
- Protocol fees: inspired by the design from Curve, $vePENDLE rewards holders with protocol revenue. This includes both the 3% of all yield accrued from YT and yield from matured unredeemed PTs.
- Incentive channeling: vePENDLE lockers will receive 80% of the swap fees for pools they voted (incentivized liquidity)
- LP Reward boost: vePENDLE holders that LP in a pool receive boosted incentives and rewards (by up to 250% based on the vePENDLE value)
More info on the veTokenomics model: https://mettalex.com/blog/ve33-the-future-of-tokenomics/
Closing thoughts
Signum Capital is proud to support the Pendle team who constantly have their heads down building to ship new features to their protocol. We are excited for Pendle v2 to see how it can scale through better composability and be the main platform for yield markets. More partnership with other protocols is already in the pipeline to expand DeFi and drive the adoption of yield trading.

